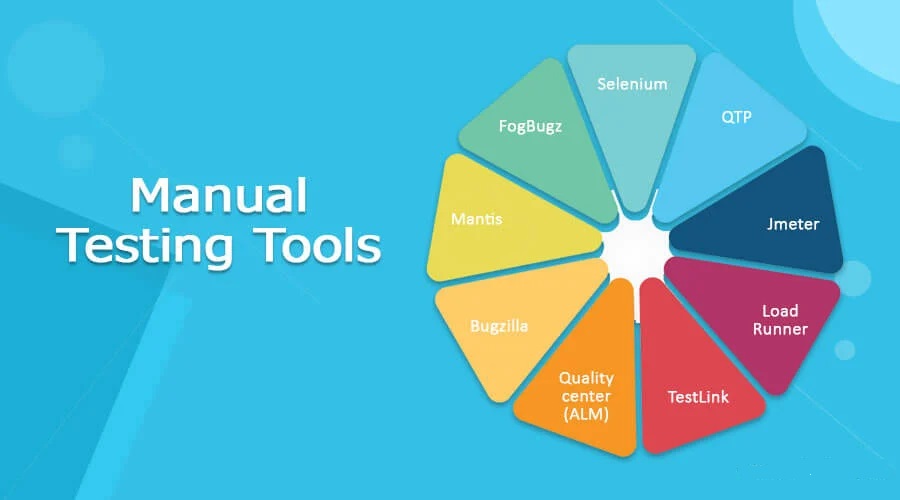
Technology
Artificial Intelligence

Artificial intelligence (AI) is a field of science that focuses on building machines and computers that can learn, reason, and act in ways that would normally require human intelligence.
AI systems use math and logic to simulate human reasoning, and learn from data to make decisions and predictions.
aws devops
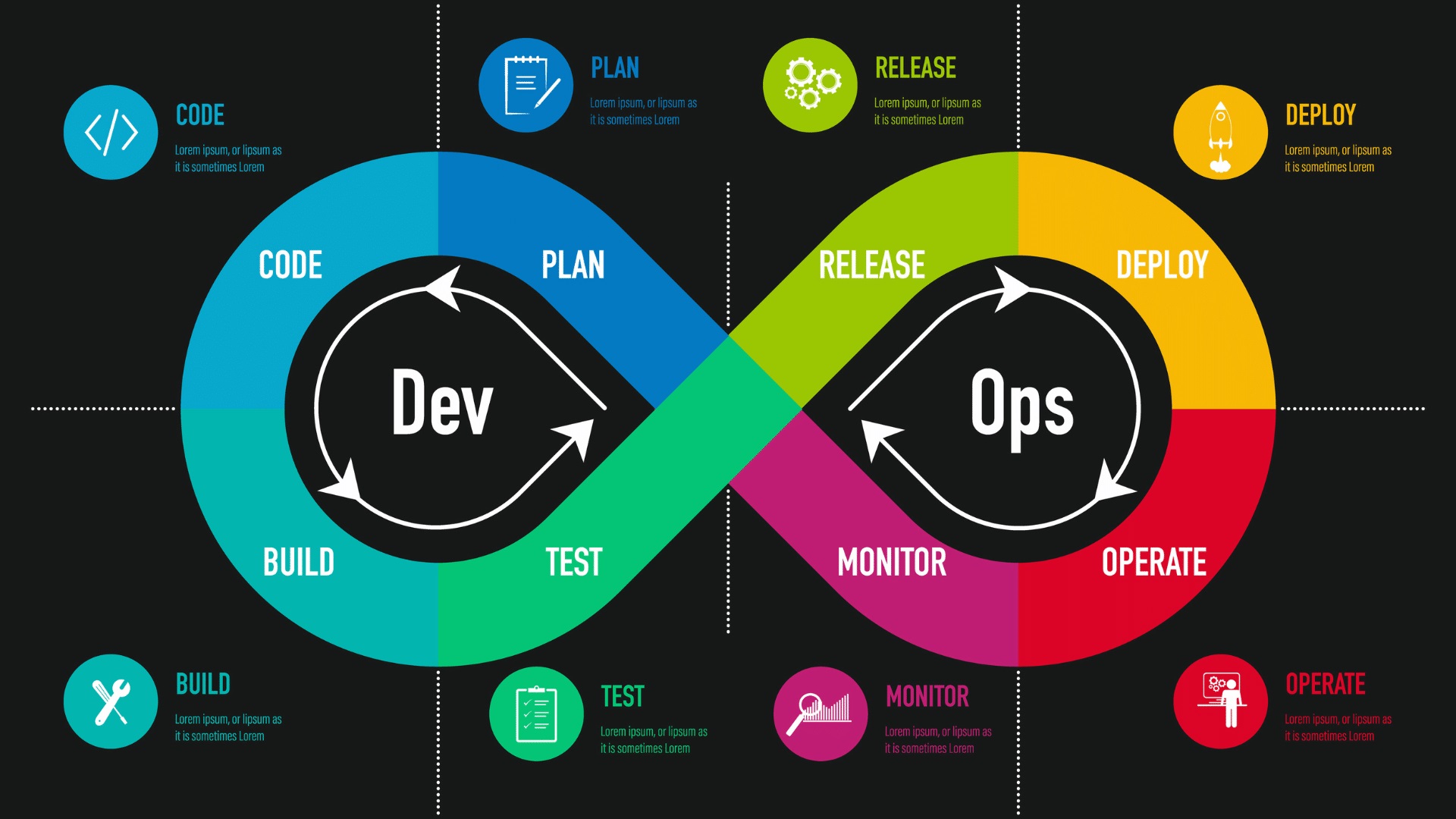
DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increases an organization’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity
evolving and improving products at a faster pace than organizations using traditional software development and infrastructure management processes
Cloud Security

Cloud security measures can be categorized as provider-based, customer-based, or service-based. Provider-based security measures are implemented by cloud service providers to protect the physical data centers and network architecture.
You can demonstrate your cloud security competency by taking the Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK), a web-based exam.
Network Engineers

Network engineers are responsible for the design, implementation, maintenance, and operation of computer networks for businesses and organizations
They work with various types of networks, including local area networks (LANs), wireless local area networks (WLANs), personal area networks (PENs), desk area networks (DANs), and voice over internet protocol (VOIP) networks
VLSI design
Embedded systems
Civil Engineering

Civil engineering is a professional field that involves designing, constructing, and maintaining the physical environment.
Civil engineers design and oversee the construction of public works, such as roads, bridges, and buildings. They also ensure that these structures are safe, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
Mechanical Engineering

Mechanical engineering is the study of how physical machines work, and how to design, analyze, and maintain them. It's a broad engineering discipline that uses physics, math, and materials science.
Design power-producing machines like engines, turbines, and generators
Design power-using machines like air conditioners and refrigeration systems
Develop manufacturing processes
Non-IT